e Invoice System in 2024: A Complete & Simplified Guide for Indian SMBs
Ever since the GST e invoice system was first introduced in 2020, businesses – large, medium and small, have had many questions and doubts about the topic. Although the government has made a deliberate effort to implement the e invoice system in phases, initially to businesses with a turnover of more than 500 Crore and now to more than 5 Crore turnovers, the whats and hows of the e invoice system are still unclear to some of you. To help such businesses struggling to understand some or all the aspects of GST e invoice, here is a comprehensive guide that takes you through the intricacies of e invoice system, its significance, the phased implementation, and its important role in the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime.
🔔 Latest e Invoicing Notifications
- Latest eInvoice Notification No:10/2023: e invoices are mandatory for businesses with aggregate annual turnover (AATO) between Rs.5 Crore and Rs.10 Crore from 1st August 2023.
- e Invoice Notification No:17/2022: e Invoices are mandatory for businesses with AATO above Rs.10 Crore from 1st October 2022.
- e Invoice Notification No:01/2022: e Invoice are mandatory for businesses with AATO above Rs.20 Crore from 1st April 2022.
Click here for the latest notifications on e invoicing by the GST Council.
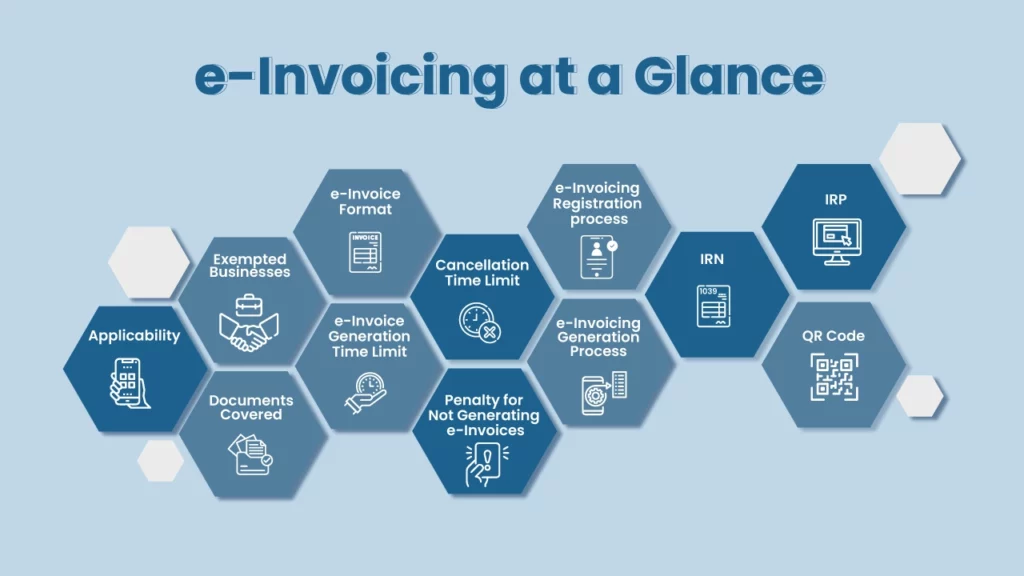
What is e Invoice System?
e-Invoicing or electronic invoicing or e Invoice system is a process of reporting invoices to the GST portal or the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP). Once a normal GST invoice is generated for a B2B transaction, specified particulars of the invoice must be entered in FORM GST INV-01 on the IRP. On successful submission, the IRP returns the invoice with a unique Invoice Reference Number (IRN) after adding a digital signature and a QR Code. This process of preparing an electronic invoice is called e-invoicing. Thus, the generated invoice is called an e invoice or gst e invoice.
As per Rule 48(4) of the CGST Act, all the registered and eligible suppliers for e-invoicing are required to generate GST e invoices before sharing them with the buyers. Any invoice generated without a valid IRN shall not be considered as an invoice.
The e-invoice system was introduced under GST with the approval of the GST Council during its 37th meeting in September 2019. e-Invoicing was implemented in phases and e invoices are mandatory for reporting business-to-business (B2B) invoices and export invoices.
To fully appreciate the evolution of the GST e invoice system, it is necessary to understand what e-invoicing is and how it has transitioned from traditional to electronic forms.
e-Invoicing Applicability: For Which Businesses GST e Invoices are Mandatory
As per GST Notification No.13/2020, a company’s Annual Aggregate Turnover (AATO) decides e-invoicing applicability. The implementation of e-invoicing has been taking place in a phased manner, with Phase-1 calling the businesses with an AATO of over 500 Crores. The threshold has been lowered in each phase, with the latest phase (Phase-6) encompassing businesses with a turnover of more than 5 Crores. The upcoming phase is yet to be announced and is expected to include businesses with an AATO of more than 1 Crore.
e Invoices thus become mandatory for registered individuals or businesses if their aggregate turnover, as determined by their PAN, exceeds the specified limit in any financial year from 2017-18 onwards. Once a company initiates the generation of GST e invoices, it must continue the same, irrespective of whether its turnover falls below the threshold limit.
Here are the different phases of e invoicing implementation along with the announcement year, e invoice limit, date of commencement and the objective.
| Phase | Month/Year of Announcement | e Invoice Turnover Limit | Applicable From | Objective |
| Phase 6 | May 2023 | Above Rs.5 Crore | 1st August 2023 | To create a more uniform and standardised invoicing process and reduce discrepancies in tax reporting. |
| Phase 5 | August 2022 | Above Rs.10 Crore | 1st October 2022 | To further digitise and streamline the invoicing process for a larger segment of businesses, |
| Phase 4 | February 2022 | Above Rs.20 Crore | 1st April 2022 | To bring a larger segment of businesses under the e invoicing framework |
| Phase 3 | March 2021 | Above Rs.50 Crore | 1st April 2021 | To expand the coverage, make e-invoicing compulsory for a wide range of businesses |
| Phase 2 | November 2020 | Above Rs.100 Crore | 1st January 2021 | To gradually expand the coverage and ensure that a broader range of businesses adopted the system |
| Phase 1 | October 2020 | Above Rs.500 Crore | 1st October 2020 | To familiarise large businesses with the e-invoicing system and encourage their voluntary participation |
Businesses Exempt From GST e Invoice System
The following categories of registered individuals are not required to issue gst e invoices even if their turnover falls under the prescribed limits:
- Special Economic Zone (SEZ) Units
- Insurers, banking companies, financial institutions (including non-banking financial companies)
- Goods transport agencies providing road transportation services
- Providers of passenger transportation services
- Providers of services related to admission to multiplex screen cinematograph film exhibitions.
The exemption from e-invoicing is for the entity but not concerning the nature of the supply/transaction.
Documents Covered Under e Invoice System
Registered businesses with an aggregate annual turnover exceeding the specified threshold must generate e-nvoices under the e invoice system for the following documents in respect of B2B Supplies and Exports –
Taxable Invoices
This includes invoices issued by registered taxpayers for the supply of goods or services, whether it’s business-to-business (B2B) or business-to-government (B2G) transactions.
Credit Notes and Debit Notes
Any credit or debit notes issued by registered businesses as a part of their transactions, including adjustments in invoice amounts, are covered under the e invoice system.
Invoice cum Bill of Supply
Businesses that provide both taxable and exempt supplies can issue an invoice cum bill of supply. This document is also part of e-invoicing.
Goods or Supplies Covered Under eInvoice System
Currently, the following supplies are covered under e-Invoicing –
- Supplies to registered persons (B2B)
- Supplies to SEZs (with/without payment)
- Exports (with/without payment) and
- Deemed Exports
B2C (Business-to-consumer) supplies are not currently covered under e-invoicing.
e Invoice Format or GST e Invoice Schema
e Invoice Schema or Form GST INV-1 is a standardised, machine-readable format for gst e Invoice. More than 300 accounting and billing software currently generate invoices in different electronic formats. These formats are not universally compatible, causing interoperability issues within the GST system. To address this, the e-Invoice Shema, a machine-readable format, was developed to facilitate uninterrupted communication. The e-Invoice format is customised for Indian business needs while aligning with international standards (UBL/PEPPOL).
Generating an e-invoice relies on approximately 140 data fields outlined in the e-invoice schema and template. Among these, around 50 data fields are marked mandatory and must be completed. The mandatory fields cover essential details such as buyer and supplier information, invoice value, tax rate, description, HSN of goods and/or services, taxable value, and tax amounts. The remaining fields pertain to payment-related information, including bank account number, payment mode, and reference document number.
The GST System does not accept the e-invoice unless all the mandatory fields are filled. The
optional items can be used by the seller and buyer as per their business needs.
e Invoice Sample Format
E-invoicing is the most effective way to track your bills in real-time and reduce errors. After you’ve prepared an e-invoice, you can submit it for approval to the Invoice Registration Portal (IRP). And after IRP verification, digitally sign it and share it with the connected buyer. You can use automated e invoice software like myBillBook to send them to your customers.
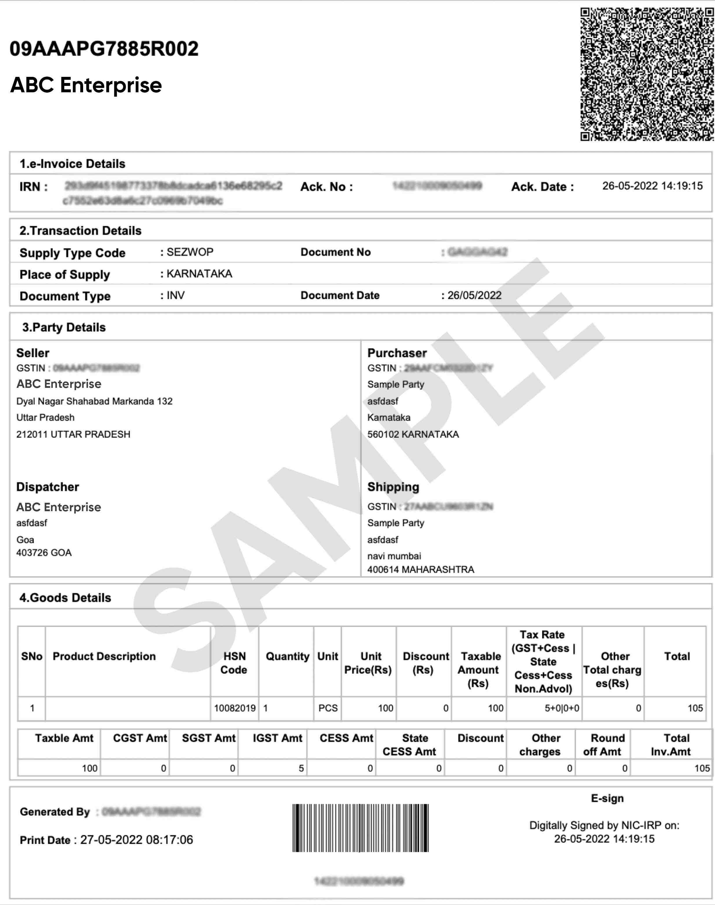
Invoice Details in JSON Format
The invoice details, as per the prescribed schema (Form GST INV-1), must be reported to IRP in JSON format. JSON, short for JavaScript Object Notation, serves as a universal language for seamless data exchange between systems and machines. ERP or accounting software will automatically generate JSON format, relieving taxpayers of any concerns. JSON is also the format used in the GST system to report all data to the GST System.
e-Invoice Generation Time Limit
When e-invoicing was first introduced, there was no time limit to report the invoices to the IRPs. However, the GST authority in April 2023 imposed a time limit of 7 days from the date of generating the invoice for taxpayers with AATO greater than or equal to 100 crores.
In the recent announcement made in September 2023, the time limit to report old invoices has been increased to 30 days from the date of generating the invoice. For instance, if you created an invoice on 1st November 2023, you can generate an e-invoice for the same till 30 November 2023. Reporting will not be allowed after 30th November. No time limit restrictions are imposed on businesses with turnover less than 100 Crores, as of now.
The new time limit restriction of 30 days has come into effect from 1st November 2023.
e-Invoice Cancellation Time Limit
Once generated, an e-invoice can be cancelled within 24 hours from the time of generation. After 24 hours, an e-invoice cannot be cancelled. Once cancelled, you cannot use the same document number or invoice number to generate a new e-invoice. You need to create a new invoice with a unique document number and report the same for e-invoice generation. e-Invoice cancellation can be done only through the e-invoice official portal.
Also, if there is any mistake or incorrect entry in the e-invoice, there is no option to modify or edit the e-invoice. The only option is to cancel it within 24 hours from the generation time. Once cancelled, you must report a new invoice with a new document number and generate a fresh GST e invoice.
Further, there is no option to partially cancel the e-invoices once generated. The only option is to fully cancel the e-invoice within 24 hours from the time of generation.
If you missed the 24-hour deadline to cancel the e-invoice, you can make the changes on the GST portal while filing GSTR-1. In case GSTR-1 has already been filed, use the amendment mechanism provided under GST.
Penalty for Not Generating GST e Invoices
Section 122 of CGST/SGST Act, which defines the offences and penalties related to invoicing and tax payments, also applies to e invoicing. According to the Act, if the registered businesses makes supplies without generating e invoices or commits any of the 21 offences mentioned in section 122 shall be punished with a penalty that shall be higher of the
following amounts:
- “The amount of tax evaded, fraudulently obtained as refund, availed as credit or not
deducted or collected or short deducted or short collected, or
- A sum of Rs.10,000.”
How to Register for e Invoicing
If you are new to e-invoicing, you need to first register your GSTIN at einvoice portal. Please note that if you already have an account in e-way bill portal, you can use the same login details for the e-invoice portal. You don’t have to create another account. For those who do not have an account, here is a step-by-step guide to registering for e-invoicing.
- Visit einvoice1.gst.gov.in/
- Click on ‘Registration’ and access the e-invoice registration form.
- Enter your GSTIN and captcha, then submit the request.
- The form will auto-fill with your business details.
- Verify the details; if correct, click ‘Send OTP.’
- Enter the OTP, click ‘Verify OTP.’
- Choose a username and set a password.
- Confirm the password and click ‘Save’ to log in.
How to Generate e-Invoice on e-Invoice Portal
Once you register for e-invoicing, you can start generating e-invoices using the free tool provided by the e-invoice portal. The einvoice portal provides a GST e-invoice preparing and printing tool (GePP) to create and print einvoices. The GePP is an Excel-based tool that can be downloaded from the einvoice portal. It is recommended for those businesses not using a billing software and require 10-12 e invoices per day. Once you download the tool, follow the below steps to generate e-invoices.
- Open the GePP tool and go to ‘Masters Menu’.
- Fill the details under ‘Supplier Profile’, ‘Receipt Master’, and ‘Product Master’
- Click on e-Invoice Menu and select ‘New Invoice’
- Fill in document, ‘Bill To’, transaction, and payment details. Some fields auto-populate when related options are selected.
- Review and submit. Preview the e-invoice.
- Confirm or edit if necessary.
- The entry file is created under ‘Pending Invoices’.
- A maximum of 10 pending invoices can be prepared for IRN generation.
- Visit ‘Pending Invoices’ and click ‘Validate’.
- Once validated, click ‘Prepare JSON’.
- The JSON file for pending invoices is generated in your tool’s location. Correct any errors displayed and re-run ‘Prepare JSON’ if needed.
- Go to einvoice1.gst.gov.in/ or einvoice2.gst.gov.in/.
- Login and from the left-side menu, choose ‘e-Invoice > Bulk Upload’.
- You’ll land on the ‘Invoice Bulk Upload’ page.
- Select ‘Browse’ to choose the JSON file.
- Click ‘Upload’ to upload the file to the system.
- The system processes the JSON file.
- Individual invoices receive IRNs separately.
- Details, including IRN and others, appear in the ‘Successfully Uploaded Invoice Details’ table on the portal.
For detailed explanation on the e-invoice generation, click here.
Special Features of the Indian e-Invoicing Framework
Invoice Registration Portal (IRP)
- An IRP, or Invoice Registration Portal, plays a crucial role in the e-invoicing system. It’s a centralised platform where businesses generate and register their invoices.
- When a seller creates an invoice, it needs to be registered on the IRP. The IRP then generates a unique Invoice Reference Number (IRN) along with a QR code and digitally signs the invoice before it’s shared with the buyer.
Unique Invoice Reference Number (IRN)
- The IRN is a unique identifier for each e invoice, computed based on essential details, including the GSTIN of the document (invoice or credit note or debit note), financial year, document type, and document number.
- The IRN, standardised across IRPs, ensures uniqueness and helps prevent duplication.
QR Code
- The IRP generates a QR code containing the IRN, essential invoice parameters, and digital signature.
- Key particulars in the QR code include GSTINs of the supplier and recipient, invoice number, date of generation, invoice value, HSN code, unique IRN, and date of generation of the IRN.
- By scanning the QR code, one can verify the authenticity of an e invoice. The GST department released a QR Code Scanner mobile app to scan the QR codes.
Digitally Signed e-Invoices
- After uploading invoice data to the IRP, the portal generates the IRN and digitally signs the e-invoice using its private key. By digitally signing the invoice, the government verifies the authenticity of the invoice details provided by taxpayers.
- This digitally signed e-invoice thus becomes a valid e-invoice, which the seller can use for business transactions.
Multiple IRPs
- To ensure uninterrupted operations, multiple Invoice Registration Portals (IRPs) are established.
- The National Informatics Centre (NIC) serves as the primary IRP, with more added over time.
- Link to IRPs
- IRP 1 – https://einvoice1.gst.gov.in/
- IRP 2 – https://einvoice2.gst.gov.in/
Multiple Modes for Reporting
- Taxpayers can report e-invoices using various modes including –
- API-based integration with taxpayer’s system directly
- API-based integration with taxpayer’s system through GSP (GST Suvidha Provider)
- Web-based and mobile app-based modes will be introduced in the future.
Benefits of having an e-Invoicing system
Businesses will benefit from e-invoicing in the following ways:
Limited Errors
The most valuable benefit of e-invoicing is the reduction of errors. E-invoicing in GST resolves and plugs a significant gap in GST data reconciliation and reduces errors.
Electronic invoice processing solutions in the e-invoice systems lessen the need for manual inputs and improve automation.
Furthermore, e-Invoices generated by one software can be read by another. As a result, it enables interoperability and significantly reduces data entry errors compared to paper-based invoices.
Easy Invoice Tracking
Another advantage of e-invoicing is the ease of tracking invoices. The e-invoicing software determines the time of sending, viewing, and paying an invoice and thereby helps in the real-time tracking of invoices.
As a result, it is simpler to confirm the delivery and receipt of an invoice.
Furthermore, certain e-invoicing service providers can assist you in determining when the customer viewed the invoice.
Reduced Tax Evasion
E-invoicing under GST (Goods and Services Tax) suggests prospects for dealing with tax evasion. E-invoicing software allows real-time access to invoice data. It contributes to the faster availability of genuine input tax credits. Hence reduces the possibility of invoice manipulation.
Furthermore, including input tax credit and output tax information in e-invoicing software can assist tax inspectors in detecting fraudulent input tax credits.
Hence, e-invoicing systems reduce the risk of false GST invoices while ensuring valid ITC (Input Tax Credit) applications.
Data Integrity
Since the information needed for audits and surveys by the tax authorities is available at the transaction level, e-invoices eliminate the risk of counterfeit bills, instantly certifying their legitimacy.
FAQs on e-Invoicing & e-Invoices
Any registered business with a prescribed annual turnover can generate e-invoices. Currently businesses with an annual turnover of more than 5 Crore must generate einvoices for all B2B and export transactions. e-Invoicing aims to enhance tax compliance, reduce fraud, and streamline business processes by standardizing invoice data. e-Invoices are standardised electronic invoices which are generated using government registration portals, while normal invoices are the regular invoices that businesses generate on their own using their billing systems. The issuer of an e-invoice is the registered supplier, seller or business. As of August 1, 2023, businesses with a turnover of more than 5 Crore are required to generate e-invoices for B2B and export transactions. Certain entities like Special Economic Zone Units, insurers, and goods transport agencies are exempt from e-invoicing. Yes, einvoices are mandatory for business-to-business (B2B) transactions. e Invoices are not mandatory for business-to-consumer (B2C) transactions. e-Invoices must be generated at the time of invoice creation; if not 30 days from creating the normal invoice. e-Invoice generation beyond 30 days is not possible. e-Invoices are generated through ERP or accounting software integrated with IRPs, you cannot generate e-invoices manually. Non-compliance with e-invoicing rules can result in financial penalties up to Rs.25,000. Yes, e-invoices are digitally signed by the IRPs for authenticity. e-invoices cannot be edited. Corrections must be made through the issuance of a credit or debit note. E-invoices cannot be deleted; they can only be canceled. Yes, Invoice Reference Number (IRN) is mandatory on e-invoices. To start generating e-invoices, visit e-invoice official websites - einvoice1.gst.gov.in/ or https://einvoice2.gst.gov.in/ Yes, a QR code with key particulars is mandatory in e-invoices for verification and authentication purposes.Who can make e-invoice?
What is the purpose of e-invoice?
What is the difference between e-invoice and a normal invoice?
Who issues e-invoices?
What is the new e-invoice limit?
Who is exempted from e-invoice?
Are e invoices mandatory for B2B?
Are e-invoices mandatory for B2C?
Can I generate E-invoice later?
How do I manually generate E-invoice?
What is the penalty for E-invoice non-compliance?
Does e-invoice require a signature?
Can we edit e-invoice?
Can we delete e-invoice?
Is IRN mandatory on an invoice?
How do I start an e Invoice?
Is a QR code mandatory on e-invoice?