Free Transport Bill Formats
Use a standard transport bill format to record freight charges, vehicle details, and consignor–consignee information for every goods movement.
- Ready formats for recording transport and delivery charges
- Helps maintain proof of goods movement and payment
- Suitable for transporters, logistics firms, and trading businesses
Powered by myBillBook - India's #1 Billing Software


What Is a Transport Bill Format?
A transport bill format is a standard document layout used to record charges and details for transporting goods from one location to another. It helps businesses, transporters, and logistics providers clearly document freight costs, vehicle information, goods description, and delivery terms for every shipment.
A properly structured transport bill format ensures transparency between the sender, transporter, and receiver, supports accurate accounting, and acts as proof of goods movement during audits or payment verification. It is commonly used for local deliveries, inter-city transport, and long-distance freight operations across India.
Download Free Transport Bill Templates
How to Create a Transport Bill Format?
Want to Invoice Faster and Smarter?
Invoice templates require manual updates and calculations.
Our free invoicing software lets you create accurate, customised invoices in just a few clicks.
What is the Purpose of Making a Transport Invoice Format?
A transport invoice is issued to formally document and charge for freight or logistics services used to move goods from one place to another. It helps transporters clearly define the service provided, calculate charges based on distance, weight, vehicle type, or trips, and avoid payment disputes.
From a compliance perspective, a transport invoice supports GST reporting, transporter records, and audit requirements. It acts as proof of service, helps track outstanding payments, and creates a transparent record between the transporter and the customer for accounting, reconciliation, and legal reference.

What is the Difference between Transport Invoices and Other Invoices?
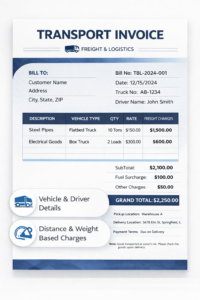
Transport Invoice Format
A transport invoice is issued for providing freight or logistics services, not for selling goods. It highlights vehicle and driver details, pickup and delivery locations, distance or weight-based charges, fuel surcharges, and transporter GST rules. It is commonly linked with LR, GR, or e-way bill documentation.
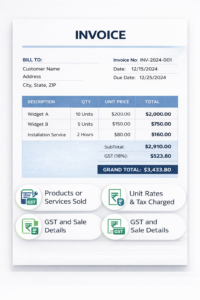
Other Invoice Format
An other invoice is issued for the sale of goods or services and represents a transfer of ownership. It includes product or service descriptions, quantities, unit prices, discounts, GST details, payment terms, and totals. These invoices serve as official records for accounting, taxation, revenue tracking, and customer billing.
What are the Essential Fields that must be Included in a Standard Transport Bill Format?
A standard transport bill format must include specific fields to ensure transparent billing, accurate records, and smooth transportation of goods. These fields help transporters and businesses avoid confusion and maintain proper documentation.
Transport Bill Number and Date
The transport bill number and date serve as unique identifiers, making it easy to track shipments, payments, and transport-related records.
Transporter Details
This field includes the transporter’s business name, address, contact information, and GSTIN if applicable, establishing responsibility for the transport service.
Consignor Details
Consignor details identify the sender of the goods and include their name, address, and tax information when required.
Consignee Details
Consignee information specifies the receiver of the goods, ensuring accurate delivery and clear ownership during transportation.
Goods Description
The goods description covers the type of goods, quantity, weight, and packaging details, helping verify the shipment contents.
Vehicle Information
Vehicle information, such as vehicle number and transport mode, supports tracking and validation of goods movement.
Freight Charges
Freight charges specify the agreed transportation cost and serve as the basis for the transport bill.
Additional Charges
This section lists additional costs, such as loading, unloading, toll fees, or handling charges, if applicable.
Total Payable Amount
The total payable amount shows the final transport charge after adding all applicable costs.
Payment Terms
Payment terms clarify how and when the transport charges are to be paid, reducing payment disputes.
Signature or Stamp
The transporter’s signature or stamp confirms the accuracy and authenticity of the transport bill.
What are the Advantages of Using a Transport Bill Format?
Using a standard transport bill format offers multiple benefits for transporters, logistics providers, and businesses involved in goods movement. It ensures clarity, consistency, and better control over transport-related transactions.
Ensures Clear Documentation
A transport bill format clearly records shipment, charges, and transporter details, reducing confusion between all parties involved.
Improves Billing Accuracy
Structured fields help calculate freight and additional charges correctly, minimising errors in transport billing.
Acts as Proof of Goods Movement
A properly maintained transport bill serves as valid evidence of the transportation of goods during audits or disputes.
Supports Faster Payments
Precise billing details and payment terms help customers process transport payments without unnecessary delays.
Simplifies Record Keeping
Standardised transport bills make it easier to store, retrieve, and manage transport records over time.
Reduces Disputes
Clearly stated charges and shipment details help avoid disagreements over freight costs or deliveries.
Helps in Business Analysis
Transport bills provide valuable data to analyse transport costs, routes, and operational efficiency.
Know More About Transport Bill Format in Word, Excel, PDF
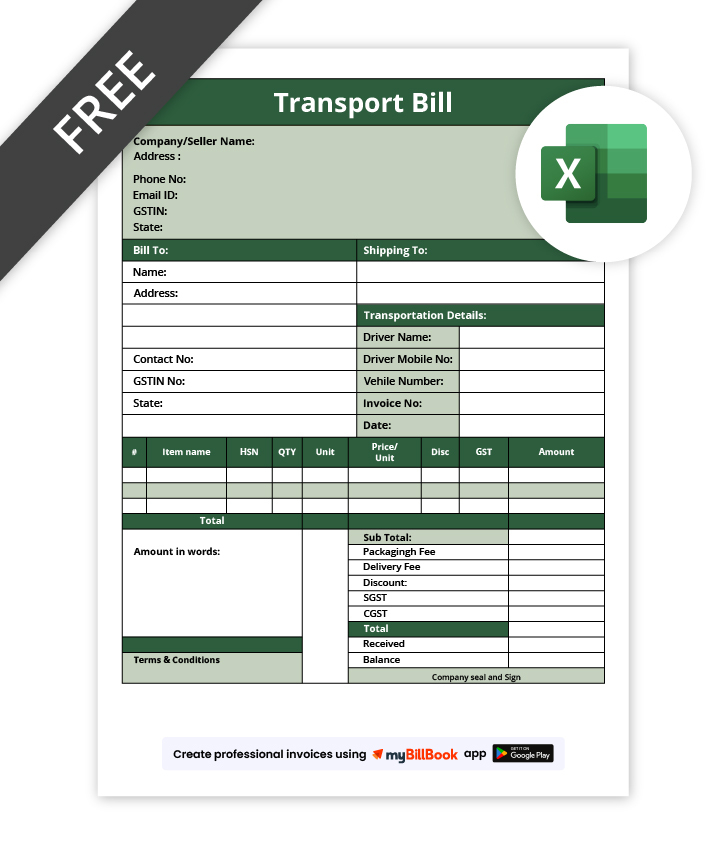
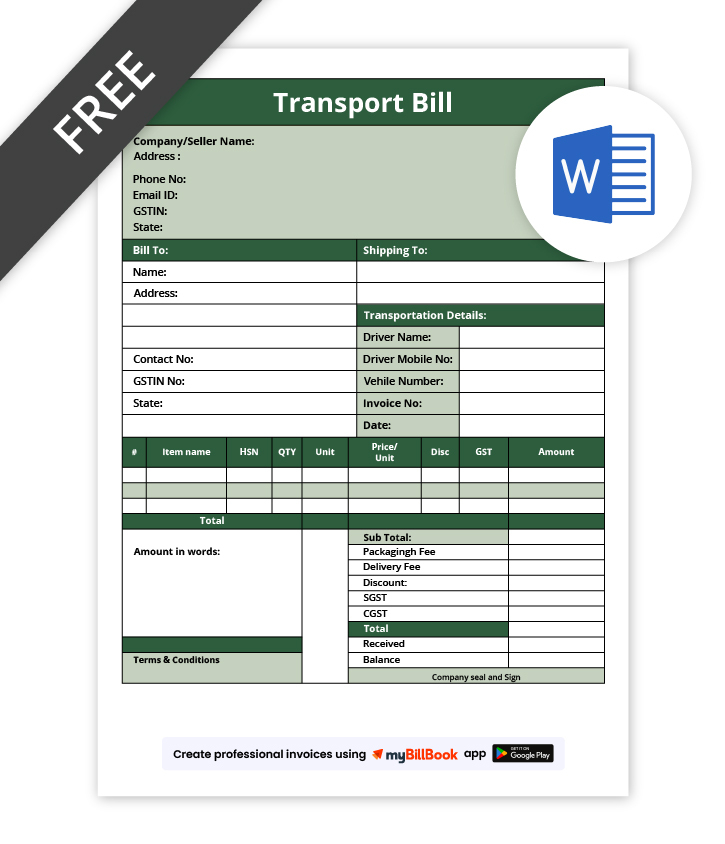
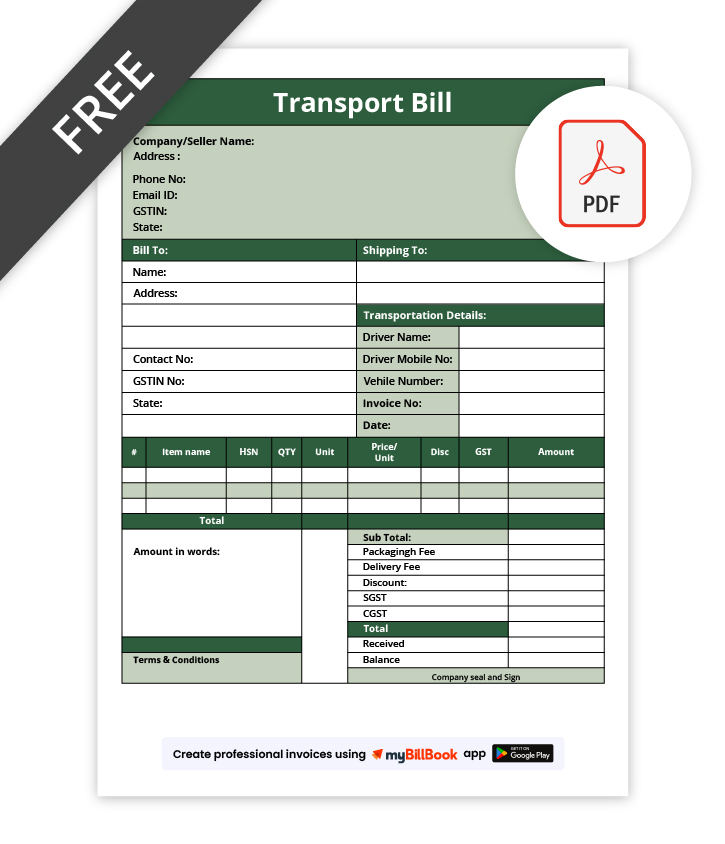
Transport Bill Format in Word
A Transport Bill Format in Word is ideal for businesses that need a simple, editable document for transport billing. It allows users to easily modify text, adjust layouts, and add or remove fields such as transporter details, goods information, and freight charges. This format is especially useful for small transporters and traders who prefer manual customisation before sharing or printing transport bills.
Transport Bill Format in Excel
A Transport Bill Format in Excel is best suited for businesses that want automatic calculations and organised data entry. It helps calculate freight charges, additional costs, and total payable amounts accurately using formulas. Excel formats are useful for managing multiple transport bills, tracking charges, and analysing transport expenses efficiently.
Transport Bill Format in PDF
A Transport Bill Format in PDF is commonly used when a final, non-editable transport bill is required for sharing or record-keeping. It preserves the layout and formatting across devices, making it suitable for sending to customers, transport partners, or auditors. PDF formats are ideal for official documentation and long-term storage of transport bills.
Thinking of upgrading how you do invoicing?
Instead of static formats, manage invoices digitally with our free invoicing software.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a transport bill format and why is it important for logistics operations?
A transport bill format is a standard document used to record shipment details (consignor/consignee, goods, vehicle, freight charges, and payment terms). It’s important because it creates a clear billing trail, supports proof of goods movement, reduces disputes, and keeps transport documentation consistent for accounting and auditing.
How do I ensure accuracy and prevent errors when filling out a transport bill format manually?
Use a simple checklist: verify bill number/date, match party names with the order/invoice, double-check goods quantity/weight, confirm vehicle number, and itemise charges clearly. Before sharing, recheck totals, payment terms (paid/to-pay), and ensure signature/stamp is added to avoid later disputes.
How can I customize a transport bill format to include company branding or additional clauses?
Add your logo, company name, address, and contact details in the header, then include a small “Terms” section at the bottom. You can also add clauses like liability limits, delivery timelines, demurrage/waiting charges, and payment due dates—keep them short and easy to understand.
How does an electronic transport bill format improve tracking and visibility of shipments?
An electronic transport bill format makes it easier to share instantly with customers, store centrally, and retrieve anytime. It also improves visibility by keeping shipment and charge details in one place, reducing phone follow-ups and making status checks faster for both shipper and transporter.
Why should businesses use an electronic transport bill format instead of traditional paper forms?
Electronic formats reduce handwriting errors, prevent lost paperwork, speed up sharing, and make auditing easier. They also help maintain uniform records across branches, drivers, and staff—especially when transport bills are created frequently.
Why is a standardised transport bill format beneficial for both shippers and carriers?
A standardised format ensures both parties see the same shipment and charge breakdown every time. It reduces misunderstandings on freight, extras, and payment terms—making approvals, collections, and dispute resolution much smoother.
Who is responsible for preparing and issuing the transport bill format in a typical shipping transaction?
Usually, the transporter or logistics provider issues the transport bill for the service provided. In some cases, a business may prepare it internally (especially for own-vehicle deliveries) and get it acknowledged by the receiver.
Who should receive copies of the transport bill format after it has been issued?
Typically, copies go to the consignor (sender), consignee (receiver), and the transporter’s records/accounts team. If a third party manages payments (agent/branch), they should receive a copy as well.
Where can I find free templates or examples of transport bill formats for different modes of transportation?
You can use ready templates that can be edited for your workflow (road transport, local delivery, intercity freight) and saved as Word/Excel/PDF. If you want a quick way to generate and store transport bills digitally, you can also use myBillBook to create structured bills, keep records, and share them easily—without maintaining multiple files.
What software or tools can automatically generate a compliant transport bill format?
Tools that support structured fields (party details, goods details, charges, and totals) help create consistent transport bills quickly. If you prefer a simple setup with easy sharing and record storage, myBillBook can be used to generate professional bills and keep them organised for future reference.
What are the potential cost savings associated with adopting a digital transport bill format?
Digital transport bills can reduce printing and stationery costs, save time spent correcting manual errors, and cut follow-ups for missing documents. Over time, faster billing, better record access, and fewer disputes can also reduce operational overhead.
What are some reputable online resources for learning more about transport bill format best practices?
Look for official references (GST/e-Way Bill documentation), logistics documentation guides, and practical accounting resources on record retention and billing controls. For implementation best practices, product help centres and templates that explain required fields can also be useful.