Balance Sheet Format
A balance sheet format is a structured way to present your business’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific date. It helps business owners, accountants, and stakeholders assess financial health, ensure compliance, and make informed decisions.
myBillBook billing solution helps you easily generate accurate balance sheets while managing billing, inventory, and reports in one place.
Features of myBillBook’s Balance Sheet Format

Auto Generation
Automatically create the balance sheet format from existing records, saving time and avoiding manual table setup. Ensures a standard, professional format that’s accurate, consistent, and ready for official reporting anytime.

Real-Time Sync
The balance sheet format updates instantly when transactions change, ensuring the formatted report reflects latest data. Eliminates mismatches between ledger entries and final presentation, maintaining accuracy for teams and periods.

GST Compliance
myBillBook aligns the balance sheet format with Indian GST context, keeping headings, groupings, and categories correct. Enables audit readiness, reducing rework during checks, tax submissions, and lender or investor reviews.
Date Flexibility
Generate the balance sheet format for any chosen date or financial period, maintaining a consistent layout for monthly, quarterly, or annual analysis without altering transactions, enabling comparable snapshots across time.

Ledger Integration
Balance sheet format automatically pulls figures from ledgers into predefined sections, ensuring correct placement of assets, liabilities, and equity in a standardized table without re-entering data or adjusting columns manually.
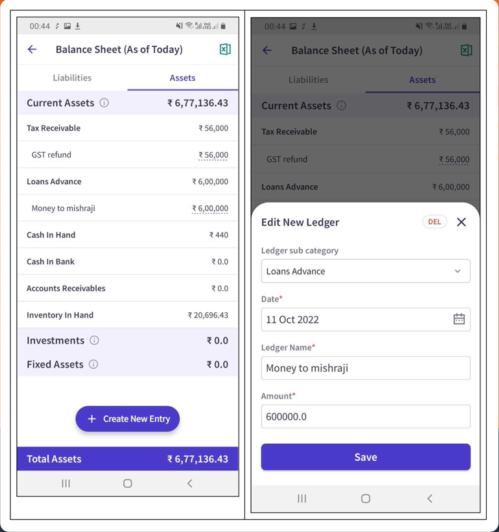
Stock Valuation
Automatically place closing stock values in the balance sheet format under current assets, using methods like FIFO or weighted average, ensuring correct presentation without manual calculations, edits, or layout changes.
Role Permissions
Control access to the balance sheet format by assigning permissions for viewing or sharing, keeping the layout secure while enabling accountants, managers, or partners to collaborate without risking unintended modifications.

Statement Linkage
Balance sheet format aligns with cash flow and profit and loss formats, preserving consistent headings and structure, enabling analysis that improves understanding and reduces effort during internal reviews and presentations.

Easy Sharing
Share the balance sheet format with stakeholders using consistent headings and layout, ensuring a presentation that builds trust, speeds approvals, and avoids confusion caused by ad-hoc spreadsheets or inconsistent tables.
What is a Balance Sheet Format?
A balance sheet format is the structured layout used to present a business’s assets, liabilities, and equity on a specific date. It follows a predefined structure so that financial information is clear, consistent, and easy to interpret.
For Indian businesses, using a proper balance sheet format ensures reports meet standard accounting practices, making them suitable for audits, tax compliance, loan applications, and investor presentations while helping owners assess their financial health.
Purpose of Balance Sheet Format
The purpose of a balance sheet format is to provide a clear and standard way to present a business’s financial position at a specific date. By dividing the report into defined sections — Assets, Liabilities, and Equity — it allows anyone reviewing the statement to quickly understand what the business owns, what it owes, and the owner’s stake in it.
A standard format ensures consistency across reporting periods, making it easier to track changes in financial health over time. It also makes comparisons simple — whether between different branches of the same company, different competitors in the industry, or different time periods for the same business.
For Indian businesses, using a proper balance sheet format offers multiple benefits:
- Compliance – Meets standard accounting principles and GST norms for audit and tax readiness.
- Credibility – Lenders, investors, and partners trust structured, professionally formatted reports.
- Decision-making – Helps owners, managers, and accountants identify financial strengths, weaknesses, and growth opportunities.
- Transparency – Offers a clear view of financial standing to all stakeholders, improving business relationships and negotiations.
How to Prepare a Balance Sheet Format
Preparing a balance sheet format is all about arranging your financial information in a structured layout so it’s accurate, professional, and easy to interpret. A proper format ensures your assets, liabilities, and equity are placed in the right sections, making the statement consistent and comparable over time.
Step-by-step process:
Select the Reporting Date
Decide the exact date for which you want to prepare the balance sheet format — usually the end of a month, quarter, or financial year. This date becomes the reference point for all figures you include.
List All Assets
Start with current assets like cash, bank balances, accounts receivable, and inventory that can be converted into cash within a year. Then include non-current assets such as property, machinery, vehicles, and long-term investments. Arrange them in order of liquidity for clarity.
List All Liabilities
Record current liabilities like accounts payable, accrued expenses, GST payable, and short-term loans due within a year. Then add non-current liabilities such as long-term debt, bonds payable, and provisions. Group them logically to match the format’s structure.
Add Equity Details
Include share capital, retained earnings, and reserves. If applicable, add the owner’s capital account and any adjustments like drawings or revaluation reserves. This section shows the owner’s stake after liabilities are deducted from assets.
Ensure the Equation Balances
Check that the total assets equal the sum of liabilities and equity (Assets = Liabilities + Equity). If the numbers don’t match, recheck entries for errors or missing figures before finalising the format.
Arrange in Standard Layout
Use a vertical format (most common in India) where assets are listed at the top, followed by liabilities and equity below. Maintain consistent headings, columns, and subheadings so the format is professional and easy to follow.
Review for Accuracy
Cross-check totals, account classifications, and formatting. Ensure the headings are clear, figures are aligned properly, and the layout meets Indian accounting standards. This step is critical for audits, loan applications, and investor reporting.
Terms You Need to Know While Preparing a Balance Sheet Format
When preparing a balance sheet format, understanding the key financial terms ensures you classify data correctly and maintain a professional, standardised layout. Here are the most important terms to know:
Assets
Resources owned by the business that have economic value. These can be tangible (cash, inventory, property) or intangible (patents, goodwill) and are usually classified into current and non-current assets.
Liabilities
Financial obligations or debts the business owes to outsiders. These include current liabilities like accounts payable and GST payable, and non-current liabilities like long-term loans or bonds.
Equity
The owner’s stake in the business, calculated as total assets minus total liabilities. It may include share capital, retained earnings, and reserves.
Current Assets
Assets expected to be converted into cash, sold, or used up within one year — such as cash, accounts receivable, inventory, and short-term investments.
Non-Current Assets
Assets that are long-term in nature and not expected to be converted into cash within a year — such as buildings, machinery, furniture, and long-term investments.
Current Liabilities
Obligations due within one year, including trade payables, accrued expenses, short-term borrowings, and current portions of long-term debt.
Non-Current Liabilities
Obligations that are due after more than one year, such as bank term loans, bonds payable, and lease obligations.
Working Capital
The difference between current assets and current liabilities. It indicates a business’s short-term financial health and liquidity.
Retained Earnings
Profits that are reinvested into the business instead of being distributed as dividends, shown under the equity section.
Accounting Equation
The fundamental principle that must always balance in the format: Assets = Liabilities + Equity.
Format of a Balance Sheet
The T-shaped or horizontal balance sheet format is as follows:
| Company Name |
|---|
| Balance Sheet | |||||
| For the Period Ended……….. | |||||
| Liabilities | Amount in Rs | Amount in Rs | Assets | Amount in Rs | Amount in Rs |
| Capital And Reserves | Fixed Assets | ||||
| Opening Capital Balance | XXXX | Land | XXXX | ||
| Reserves and Surplus | XXX | Less Depreciation | (XX) | XXXX | |
| Less Drawings | (XXX) | ||||
| Capital Balance | XXXX | Building | XXXX | ||
| Less Depreciation | (XX) | XXXX | |||
| Secured Loans | |||||
| Long term debt | XXX | Investments | |||
| Other long term liabilities | XXX | Long term Investments | XXX | ||
| Unsecured Loans | Current Assets, Loans and Advances | ||||
| Cash credit payable | XXX | Inventory | XXX | ||
| Cash and cash equivalents | XXX | ||||
| Current Liabilities | Other current assets | XXX | |||
| Trade Payables | XXX | ||||
| Accrued Interest | XXX | Prepaid expenses | XX | ||
| Other Current Liabilities | XXX | Miscellaneous expenditure | XX | ||
| Total Liabilities | XXXX | Total Assets | XXXX |
The new balance sheet format is also referred to as the “vertical format balance sheet,” as it begins with equity and liabilities and concludes with assets.
With a solid understanding of a balance sheet and its formats and details on how to create a balance sheet, you’ll be able to make informed business decisions and keep track of your company’s financial health.
It may appear complicated due to the abundance of jargon, yet it could be more sophisticated than they sound. However, once you understand the meaning of the financial statements, analysing the balance sheet is quite simple.
Common Mistakes in Preparing a Balance Sheet Format
Even with a proper balance sheet format, errors can creep in if the data is not handled carefully. These mistakes not only make the report inaccurate but can also lead to compliance issues and poor decision-making. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
Incorrect Classification of Items
Placing assets, liabilities, or equity in the wrong section of the format can lead to a misleading financial picture. For example, listing long-term loans under current liabilities distorts liquidity ratios.
Ignoring Accruals and Prepayments
Many businesses forget to include accrued expenses, prepaid expenses, or outstanding incomes in the format, resulting in incomplete financial reporting.
Not Matching the Accounting Equation
A balance sheet format must always satisfy the formula Assets = Liabilities + Equity. If it doesn’t balance, it means there are missing entries or calculation errors.
Outdated or Incomplete Data
Using old figures or failing to include recent transactions in the balance sheet format results in reports that don’t reflect the business’s actual financial position.
Inconsistent Headings and Layout
Changing headings or structure between reporting periods makes it harder to compare performance. A standard, consistent format should be followed for accurate trend analysis.
Omitting Stock Valuation Adjustments
Not updating closing stock values or using incorrect valuation methods (like FIFO or weighted average) leads to errors in asset reporting.
Ignoring Depreciation
Skipping depreciation entries for fixed assets inflates asset values and presents an unrealistic financial position in the balance sheet format.
Not Reconciling Ledgers
If party-wise ledgers are not reconciled before preparing the format, mismatches in receivables or payables may appear in the final report.
Benefits of Using myBillBook’s Balance Sheet Format
Instant Report Creation
myBillBook automatically generates your balance sheet format based on existing transactions, eliminating the need to manually prepare tables or rearrange figures. This saves hours of work and ensures professional formatting every time.
Accurate & Error-Free
The software’s automated calculations ensure that each figure in the balance sheet format is directly drawn from your recorded sales, purchases, expenses, and stock values, reducing the risk of manual errors or mismatched totals.
Always Up-to-Date
Any time you add or update transactions, the balance sheet format is refreshed instantly. This means you always have the latest figures ready for decision-making, investor presentations, or loan applications.
GST-Ready Layout
myBillBook’s balance sheet format follows Indian GST compliance guidelines. All categories, groupings, and headings are arranged to match audit requirements, making tax filing and statutory reporting smooth and stress-free.
Integrated Ledger Data
Figures from your party-wise ledgers are pulled directly into the correct asset, liability, and equity sections in the balance sheet format, ensuring a clean, complete, and properly classified financial report.
Easy Period Comparison
Quickly generate balance sheet formats for multiple time periods — monthly, quarterly, or annually — to analyse trends, track financial growth, and identify patterns without creating new layouts from scratch.
Professional Presentation
The balance sheet format is designed with clear headings, proper alignment, and standardised classifications, making it look professional and credible for auditors, bankers, and potential investors.
Secure Access Control
Control who can view, edit, or share the balance sheet format. This ensures that sensitive financial information is shared only with authorised people, such as accountants or business partners.
Quick Sharing Options
Export the balance sheet format as a PDF or share it directly via email or WhatsApp. This helps you respond faster to auditor requests, loan applications, or investor queries.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which balance sheet format is used in India?
In India, the most common format is the vertical balance sheet format, which lists assets at the top followed by liabilities and equity, in line with Schedule III of the Companies Act, 2013.
What are the 3 main parts of a balance sheet format?
The three main parts are Assets, Liabilities, and Equity. These sections follow the accounting equation Assets = Liabilities + Equity to ensure accuracy and balance.
What is the difference between vertical and horizontal balance sheet formats?
A vertical format lists items in a single column from top to bottom, while a horizontal format (T-shape) presents assets on the left and liabilities & equity on the right.
Can small businesses use a standard balance sheet format?
Yes, small businesses in India can use a simplified vertical format to record key assets, liabilities, and equity without unnecessary complexity, making compliance and reporting easier.
How often should I prepare a balance sheet format?
Most businesses prepare it annually for statutory purposes, but monthly or quarterly preparation is recommended for internal financial tracking and better decision-making.
What details should be included in a balance sheet format?
It should include current and non-current assets, current and non-current liabilities, and equity details like share capital, retained earnings, and reserves, all arranged in a consistent layout.
Is the balance sheet format different for companies and proprietorships?
Yes. Companies in India follow Schedule III guidelines under the Companies Act, while proprietorships can use a simpler format without extensive disclosures.
Can I prepare a balance sheet format without accounting software?
Yes, but using software like myBillBook automates calculations, ensures GST compliance, and formats the report professionally, saving time and reducing errors.
Why is a standard balance sheet format important?
A standard format ensures accuracy, consistency, and compliance with accounting norms, making it easier for banks, investors, and auditors to review and trust your financial reports
Know More About Bill Formats

