Journal Account Format
A journal account format captures financial transactions systematically. It helps businesses maintain accurate records for bookkeeping and financial reporting. This format can be created in Word, Excel, or PDF, and myBillBook simplifies the process with automated features.
✅ Quick & Easy Journal Entry Generation
✅ Customisable Templates
✅ Professional Look
✅ Unlimited Journal Entries
✅ Affordable Plans Starting INR 399/Year
Journal Account Formats in Word, Excel & PDF | Download Free
Features of myBillBook Journal Account Format

Smart Journal Entry Creation
myBillBook provides a structured format for journal entries, automatically aligning them with accounting standards. Users can enter transaction details, and the system ensures accurate categorization of debits and credits. This feature helps maintain consistency across all entries and reduces manual errors.

Error-Free Double-Entry System
The platform enforces the double-entry bookkeeping principle, ensuring that every financial transaction has equal debit and credit components. This minimizes discrepancies and helps businesses maintain accurate financial records without manual reconciliation efforts.
Bulk Entry Upload
Businesses dealing with a high volume of transactions can save time by uploading multiple journal entries at once. myBillBook supports bulk data imports from Excel or CSV files, allowing for seamless integration with existing financial records.

Flexible Categorisation & Filtering
Users can categorize journal entries based on transaction type, account name, or date, making it easier to locate specific records. Advanced filtering options allow for quick searches and organized financial reporting.

Secure Cloud Backup & Access
All journal entries are securely stored in the cloud, ensuring data safety and accessibility from multiple devices. Businesses can retrieve records anytime, preventing loss of critical financial data and enabling seamless remote accounting.
₹217
Per month. Billed annually
Diamond Plan
✅ Create unlimited invoices
✅ Add up to 1 business + 1 user
✅ Inventory management
✅ App + Web support
✅ Priority customer support
✅ GSTR reports in JSON format Popular
₹250
Per month. Billed annually
Platinum Plan
Everything on Diamond Plan +
✅ Add up to 2 business + 2 user
✅ 50 e-Way bills/year
✅ Staff attendance + payroll
✅ Godown management
✅ Whatsapp and SMS marketing Popular
₹417
Per month. Billed annually
Enterprise Plan
Everything on Platinum Plan +
✅ Custom invoice themes
✅ Create your online store
✅ Generate and print barcode
✅ POS billing on desktop app
✅ Unlimited e-Invoices & e-Way bills Popular

₹399 per year
Silver Plan for Android App
✅ For 1 device, 1 business and 1 user
What is a Journal Account Format?
A journal account format is a systematic method of recording financial transactions in accounting. It serves as the first step in the accounting cycle, capturing business transactions in chronological order before they are transferred to the ledger accounts. The primary purpose of a journal is to provide a clear and organized record of all financial activities, ensuring accuracy, accountability, and compliance with accounting principles.
Each journal entry consists of multiple elements, including the transaction date, accounts involved, debit and credit amounts, and a brief narration explaining the transaction. The journal follows the double-entry bookkeeping system, ensuring that every debit entry has a corresponding credit entry of equal value. This structure helps businesses maintain balanced financial records and prevents discrepancies in accounting.
Types of Entries in Journal Account
Journal entries are categorized based on the nature of the transaction. The major types include:
- Opening Entries
These entries are recorded at the beginning of an accounting period to carry forward balances from the previous period. They include assets, liabilities, and capital accounts. - Transaction Entries
These are the most common journal entries used to record daily business transactions, such as sales, purchases, expenses, and revenue. - Adjusting Entries
Made at the end of an accounting period, these entries adjust income and expense accounts to reflect accruals and deferrals, ensuring accurate financial statements. - Closing Entries
These entries are used to close temporary accounts like revenues and expenses at the end of an accounting period, transferring their balances to permanent accounts. - Transfer Entries
Used to shift amounts between different accounts, such as moving funds between departments or adjusting intercompany transactions. - Rectifying Entries
When errors occur in previous journal entries, rectifying entries correct those mistakes by reversing incorrect amounts and posting the correct transaction.
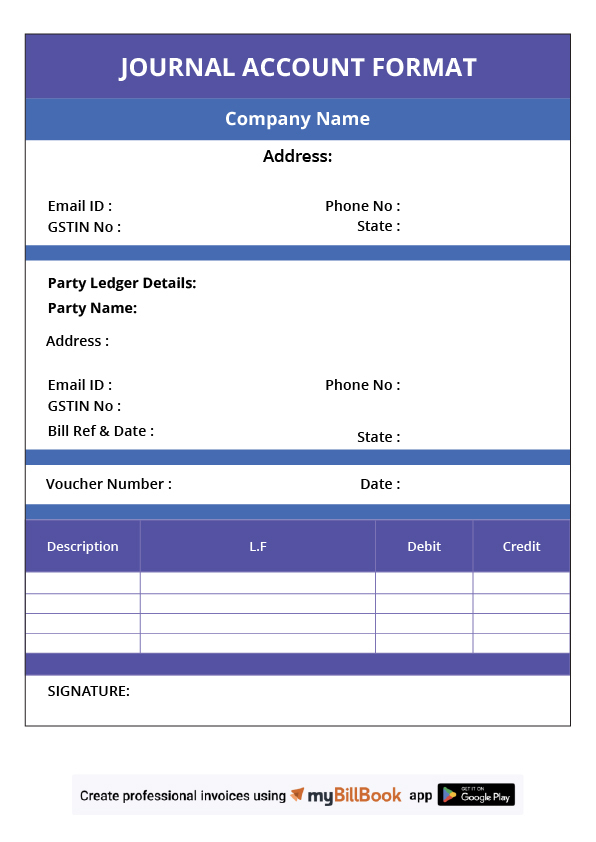
Format of Journal Account
The journal account format follows a structured approach to ensure the accurate and chronological recording of transactions. It consists of the following essential components:
- Date: This column records the date on which the financial transaction occurred. Maintaining a sequential date order is essential for accurate bookkeeping.
- Particulars: This section details the accounts affected by the transaction. The debit entry is written first, followed by the credit entry, which is preceded by “To.”
- Ledger Folio (L.F.): The ledger folio column is used for referencing, and linking the journal entry to its corresponding ledger account page. This helps in the quick retrieval of ledger details.
- Debit Amount: The amount debited in the transaction is recorded here. Debits generally represent asset increases or expense transactions.
- Credit Amount: The corresponding credited amount is listed in this column. Credits usually reflect revenue, liability increases, or equity.
Example:
| Date | Particulars | L.F. | Debit (INR) | Credit (INR) |
| 01/03/2024 | Cash A/c | 101 | 10,000 | |
| To Sales A/c | 202 | 10,000 | ||
| (Sales made) |
The format follows the golden rules of accounting, ensuring that every transaction follows the correct debit and credit treatment. This structured format not only maintains financial clarity but also simplifies audits and compliance processes.
Journal Account Format in Word, Excel, & PDF
Journal Account Format in Word:
A journal account format in Word is primarily used for documentation and printing. Users can create a structured journal format by inserting tables and customizing column widths to fit the necessary details. This format is ideal for businesses that require professionally printed copies of their journal entries for record-keeping and presentation.
Journal Account Format in Excel:
Excel is the most preferred format for maintaining journal entries due to its flexibility in performing calculations and organizing large datasets. Users can set up formulas for automatic debit and credit balancing, use pivot tables for categorization, and apply conditional formatting to highlight discrepancies. Excel also allows easy modification of entries, making it a dynamic option for financial record-keeping.
Journal Account Format in PDF:
The journal account format in PDF is used for secure and consistent formatting when sharing or storing financial records. Once journal entries are finalized, converting them into PDF ensures that no further changes can be made, preserving the integrity of financial data. This format is widely used for compliance and audit purposes, as it maintains document authenticity and prevents unauthorized edits.
Key Elements of a Journal Entry
A journal entry consists of the following essential elements:
- Transaction Date: This indicates the date when the financial transaction took place. Maintaining accurate dates ensures proper chronological order and simplifies auditing.
- Accounts Involved: Every transaction affects at least two accounts—one is debited, and the other is credited. Clearly mentioning the accounts involved helps in maintaining transparency.
- Debit and Credit Amounts: The transaction amount is recorded under debit or credit as per the double-entry bookkeeping principle. This ensures that the accounting equation remains balanced.
- Narration (Brief Description): A short explanation is included for every journal entry to describe the nature of the transaction. This helps in understanding the purpose of the transaction when reviewing records.
- Ledger Folio Reference: This provides a reference to the corresponding ledger accounts, making it easier to track transactions across the accounting system.
Best Practices for Creating & Using Journal Entries
- Maintain chronological order: Always record transactions in the order they occur to ensure clear financial tracking and simplify audits.
- Ensure debit and credit balance: Verify that total debits equal total credits in every entry to prevent discrepancies.
- Use clear and concise narrations: Provide brief but descriptive explanations for transactions to enhance transparency and understanding.
- Regularly review journal entries: Periodically check records for errors and make necessary adjustments before posting to ledgers.
- Keep supporting documents: Maintain invoices, receipts, or agreements to validate journal entries and ensure compliance.
- Leverage accounting software: Use tools like myBillBook accounting software to automate entries, reduce errors, and enhance efficiency.
FAQs
What is the purpose of a journal account?
A journal account is used to record financial transactions in chronological order. It serves as the first step in the accounting cycle before posting entries to the ledger, ensuring accurate bookkeeping and financial tracking.
What are the key components of a journal entry?
A journal entry typically includes the date of the transaction, the accounts involved, debit and credit amounts, a brief narration, and a ledger folio reference for easy tracking.
How does the double-entry bookkeeping system work in journal accounting?
In the double-entry system, every transaction has equal and opposite effects in at least two accounts. One account is debited, and another is credited, ensuring that the accounting equation remains balanced.
What are adjusting entries, and why are they necessary?
Adjusting entries are made at the end of an accounting period to account for accrued expenses, prepaid expenses, and unearned revenues. These entries help ensure accurate financial statements by aligning recorded transactions with actual financial activity.
How can accounting software help with journal entries?
Accounting software like myBillBook automates journal entry recording, ensures error-free double-entry bookkeeping, provides ledger integration, and allows users to generate financial reports seamlessly.
Know More About Accounting & Billing Formats





