What is the full form of CIN ?
Full form of CIN is Corporate Identification Number.
[adinserter block=”3″] [adinserter block=”4″]
What is CIN number?
CIN is a number that is given by the Registrar of Companies, ROC, to identify companies better via their CIN number directly.
CIN-provided companies can be public, private companies, one-person companies, not-for-profit companies, companies owned by the government or the state, Nidhi companies etc.
In short, most companies registered in India will have a Corporate Identification Number, CIN. They must include this in papers filed to the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA), mainly audits and reports.
What is the Importance of CIN?
Every company need a CIN for the following reasons:
Tracking of Transactions
CIN helps the Registrar of Companies, ROC, follow the workings of the companies. In addition, it gives the ROC a better idea of all the transactions that have taken place due to the CIN, making work easier for all parties involved.
Identification of Business Details
CIN’s 21-digit code is unique to each business. Hence, it becomes easy to identify the primary information of companies like the state of registration, essential nature of the business, and the nature of incorporation with just their CIN.
Understanding of Corporate Identity
CIN is an ID Card for businesses that help identify and separate other businesses and companies.
[adinserter block=”3″] [adinserter block=”4″]
Breaking down of 21 digits in CIN
CIN number means the Corporate Identification Number or the 21-digit unique alphanumeric number given to all businesses and companies is unique, and a company can never repeat it.
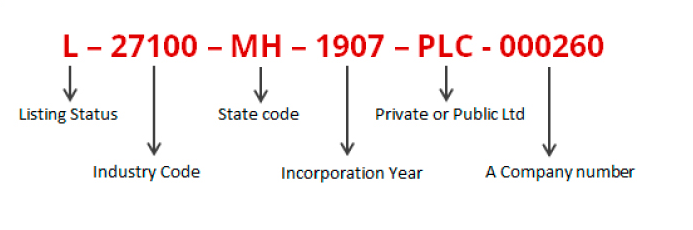
These 21 digits give off certain primary information on a business. Here is the breakdown of the 21 digits in the CIN:
- L or U: The first letter of CIN would be either “L” or “U”. The letter “U” represents an unlisted company. On the other hand, if the company is listed, it is represented by the letter “L”.
- Economic activity: The following five alphanumeric code of the CIN mentions the company’s economic activity or nature of business. Using the digits, you can recognise what industry the company will work in and what is the basic nature of their business via these five alphanumeric digits. This number is allotted by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, MCA, as they have codes for every nature of the business.
- State Code: This code in CIN represents the state of the registered business or company. Every state has two letters of identification attached to them. So, for example, for a business registered in Maharashtra, the state code would be MH which will be a part of the CIN.
- Year of incorporation: The following four digits in the CIN are the year the company was incorporated and registered. For example, if you registered a company in 2001, CIN will include those numbers.
- Classification of the company: The following three alphanumeric digits in the CIN mention the company’s classification. These digits represent whether the company is a public company, a private company, and so on.
- PTC – Private Limited Company
- PLC – Public Limited Company
- OPC – One Person Company
- FTC- Financial Lease Company (Subsidiary of any foreign company)
- GOI- Government of India(owned by the government)
- FLC- Financial Lease Company as Public Limited
- GAP: General Association Public
- GAT: General Association Private
- SGC: Companies owned by State Government
- ULL: Public Limited Company with Unlimited Liability
- ULT: Private Company with Unlimited Liability
- NPL: Not-for-Profit License Company
And so on. These represent what the classification of the company is.
- Registration by ROC: The last six numbers in the CIN Number is the registration number given by the Registrar of Company, ROC.
[adinserter block=”3″] [adinserter block=”4″]
Penalty for non-compliance with mentioning CIN
Not meeting the conditions mentioned on the CIN will let you face a penalty of INR 1,000 per day, and every officer is in default as long as the default persists. The highest penalty for this default, however, is INR 100,000. Therefore make sure to have a CIN number checked to refrain from penalty.
Where is CIN mentioned and used in business?
CIN number is an official business registration number, and the Corporate identity number is included in the following:
- Letterhead of the company
- Invoices and receipts of the company or the business
- Memos notices and every e-form submission on the MCA portal
- Annual Reports of the company also in case of annual public reports
- Transactions that can be viewed by the ROC too
Changes in CIN
Suppose a company goes through a transition process such as unlisted to listed or change in nature of business. In that case, the CIN will have changed to represent the latest information about the business or the company.
And you can make the change by contacting the Registrar of Company, ROC.
[adinserter block=”3″] [adinserter block=”4″]
[wp-faq-schema title=”FAQs about CIN”]
