Types Of GST In India
India is a federal nation with taxation authority granted to the Union and the States. According to the Constitution, both governments have separate responsibilities for which they must raise tax revenue.
The Goods and Services Tax Act, passed by parliament on March 29, 2017, levies a complete, multi-stage tax on every value addition. The GST Act took effect on July 1, 2017. It is very important because both the Central Government and the State Government depend on indirect tax revenue from the GST. The tax structures are adopted to allow taxpayers to claim credits against one another, ensuring “One Nation, One Tax.”
Various Types of GST
- The Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST)
- The State Goods and Services Tax (SGST)
- The Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST)
- The Union Territory Goods and Services Tax (UTGST)
1. The State Goods and Services Tax (SGST)
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) administered by a state is the SGST. It applies to transactions occurring within its geographical boundaries. Under the new system, formerly applicable state taxes, including the entertainment tax, value-added tax, and state sales tax, have been obsolete. It may be determined by the transactional worth of a product or the amount the purchaser must pay. When products and services are supplied within a state, businesses must charge their Customers State GST and Central GST.
Because each state has its regulations, the SGST components may vary from state to state. Specific characteristics, like taxable activities, valuation, classification of products and services, and measures, are, on the other hand, uniform across the nation. A portion of the SGST revenue is only available to the state government.
SGST applicable to several products
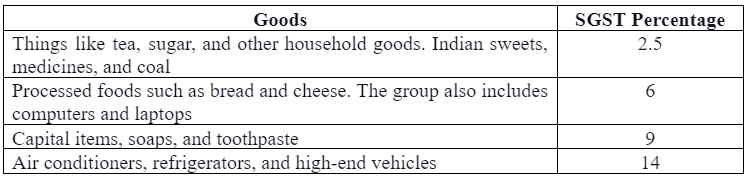
2. Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST)
Intrastate (within the same state) trades of goods and services are subject to the Central Goods and Services Tax, a tax based on the GST. The provisions of the CGST Act govern the CGST. The central government collects CGST. It replaced all previous federally imposed taxes. As a result, the state and central governments receive a portion of the revenue.
The Central Government ensures that the CGST takes the place of all other Central taxes, such as State Tax, CST, SAD, etc. Therefore, the prices of products and services charged under the CGST correspond to the basic market price.
Applicable CGST on several products

3. The Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST)
The tax known as IGST is a tax that is levied on goods and services carried across states. It is often used for transactions between two states, called “interstate transactions.” GST is charged when goods and services are sold between two states, exported, or imported into the country (IGST + customs). The IGST Act puts the responsibility for its collection primarily in the hands of the central government. When taxes are collected, the central government distributes them among the states.
IGST applicable to various products
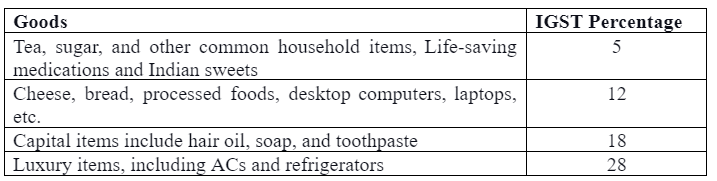
4. The Union Territory Goods and Services Tax (UTGST)
The purpose of imposing UTGST on intra-UT sales of products and services is to collect tax to give the same benefits as SGST. The UTGST is the same as India’s State Goods and Services Tax (SGST). It is charged on the delivery of goods and services (UTs). Products shipped to the Andaman and Nicobar, Lakshadweep Islands, Daman Diu, Dadra, Chandigarh, and Nagar Haveli are subject to this taxation. It is important to note that the UTGST applies exclusively to Union Territories without a legislature. Consequently, the percentage of the UTGST is equivalent to the percentages of the SGST, which are 2.5 per cent, 6 per cent, 9 per cent, and 14 per cent, respectively.
Applicable UTGST on various products
In the UTs, the Central Government is responsible for collecting this tax, which replaces the Goods and Services tax levied by the individual states. Consequently, the UTGST rate is comparable to the SGST percentages of 2.5 per cent, 6 per cent, 9 per cent, and 14 per cent.
FAQs on GST
What is the highest allowable amount for the CGST?
The Central Government of India collects Central Goods and Services Tax or CGST, which applies to all intrastate sales of goods and services. The CGST Act specifies a maximum CGST rate of 14%, which governs this.
Who is charged with collecting SGST?
The central government would collect SGST per the GST law.
What is an example of IGST?
The IGST will be applied to any commodities brought into Kerala from the state of Tamil Nadu. According to the authorities' rates decided upon, the revenue that the IGST generates is shared between the state government and the central government.
What are the 3 types of GST?
Currently, four types of GST are applicable in India: UTGST, CGST, IGST, and SGST.
In which state does UTGST apply?
The UTGST applies to purchases made in Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Chandigarh, Lakshadweep, Daman and Diu, and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
What are the five types of GST slabs?
Apart from the 4 GST slabs imposed on products and services, the 5th one is imposed on Gold items which is 3%. However, the precious and semi-precious stones do add an additional 0.25% GST.

